Low and Away and James Wood

Up and in, low and away. That’s how you attack hitters. That’s always been how you attack hitters. There are exceptions, of course. Some hitters struggle with low-inside pitches, so they see more of them. Some hitters are so feeble that pitchers just pump fastballs down the middle and dare them to do their worst. Some pitchers just throw their best pitch and don’t bother worrying about the hitter at all. But most of the time, it’s up and in, low and away. Ben Clemens wrote about a version of this yesterday, in a piece that focused on the data behind why pitchers throw inside fastballs. And the toughest inside fastballs to hit are those thrown up and in.
Pitchers have been throwing hard stuff up and in for as long as they’ve been throwing hard stuff, but Statcast’s new bat tracking data allowed us a new peek at why that’s such a successful game plan. The heat map for bat speed below is extra red because it belongs to Aaron Judge, but insofar as the least red spot is the high-inside strike, it might as well belong to any hitter.
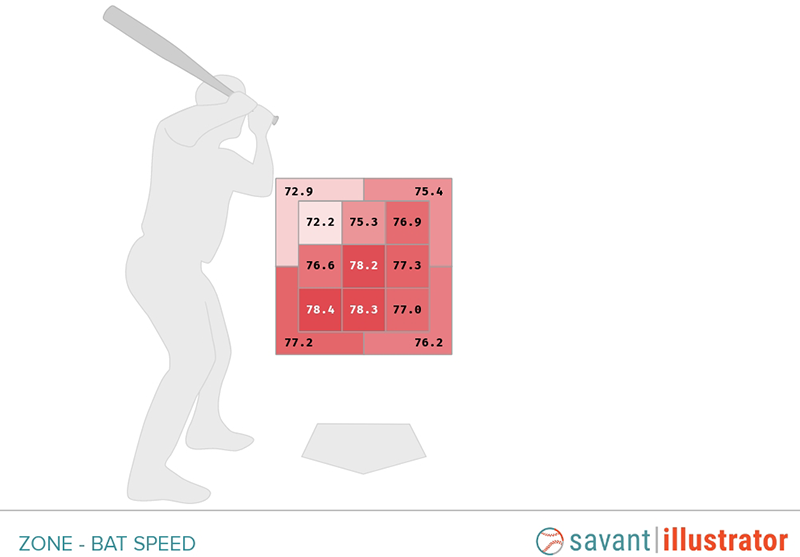
It’s harder to get your bat around up there. It requires a stiffer, more rotational (as opposed to linear) swing. You can’t get your arms extended. You can’t drop your bat head on the ball. Bust somebody up and in with something hard, and they’ll have a tough time catching up to it; now confirmed by science.
Because we are not Ben Clemens, we’re going to focus on down and away today, and we’re going to focus on batters. As you can see from Judge’s heat map, bat speed tends to be slower down there too. We’re no longer just talking about getting your arms extended. You have to modify your swing to reach pitches that far away, bending and reaching, slowing down your bat because the optimal contact point is deeper. If there’s one thing we’ve learned from bat tracking data, it’s that those kinds of adjustments make you hemorrhage bat speed. Low and away is also where trickier pitches like offspeed and breaking balls tend to end up. Nobody is good against those pitches, and I do mean nobody.
See the spot in the heat map that says 77.0 mph, inside the strike zone, but on the outer third and in the bottom third? Since 2008, 225 left-handed batters and 297 right-handed batters have seen at least 500 pitches in that low-and-outside box. According to Baseball Savant’s run values, not one of those players has a positive run value against those pitches. Not one! Every single player has been below average in that particular box, and that’s not true of any of the other 12 boxes. The two players who have come closest to breaking even on those low-and-outside strikes are Hall of Famer David Ortiz, who has been worth -0.08 runs per 100 pitches, and future Hall of Famer Mike Trout, who has been worth -0.4. It’s just not possible to perform well against that pitch (at least not without eschewing the rest of the strike zone, but no one would ever do that), even if you’re literally Mike Trout.
So we’ve established that the low-outside strike is hard to hit. It took 500 words, but we’re here now. The heat map below belongs to James Wood, and it’s part of the reason we’re talking about pitching people low and away. The numbers in this heat map show run value per 100 pitches, and they show why Wood is the poster boy for difficulty down and away.
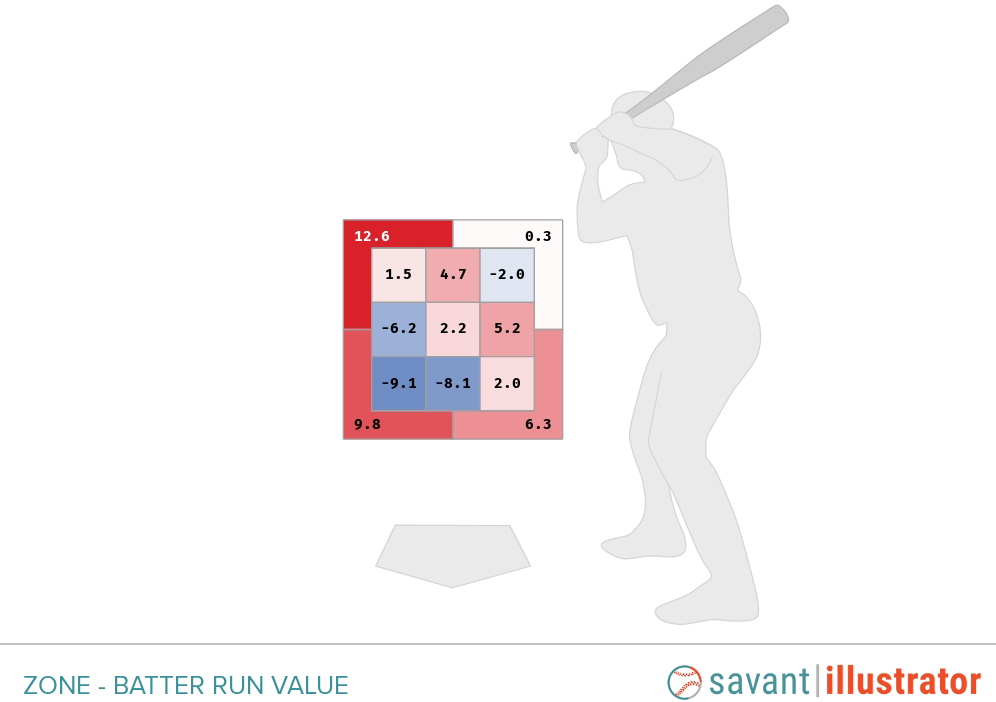
After a season and a half in the majors, Wood is the proud owner of 4.6 WAR, a 125 wRC+, and one of the most explosive swings in the game. That’s amazing. He’s just 23 years old. He looks like he will be great for at least another decade. He’s also the owner of this particularly lopsided heat map. He’s patient to a fault, which means that he’s excellent on pitches outside the strike zone. He’s great when he can get his long arms extended or when he can drop his bat head on the ball. But throw him something, anything down and away but still inside the zone, and he turns into a (very imposing) pumpkin.
If you’re a regular FanGraphs reader or just a fan of the Nationals (or Padres), you’ve likely known the book on Wood since long before he actually debuted in Washington. He’s really big. He hits the ball really hard. He hits it on the ground. He whiffs a lot too. Major league pitchers knew the book as well, and they most definitely saw some earlier version of that heat map the second the Nationals called Wood up in July 2024.
I can say that for certain because even though he was just a 21-year-old rookie, 24.2% of the pitches Wood saw were located in those three blue boxes. Among players who saw at least 1,000 pitches, that was the highest rate in baseball (switching the side of the plate around for right-handers, of course). In 2025, that rate fell to 23.8% and Wood fell to third place, behind Dansby Swanson (24.5%) and Tommy Pham (24.2%). What those numbers mean is that from the moment he debuted, pitchers have known that the only way to attack Wood was to stay the hell away from his gigantic bat. Aim for the outside corner, keep it low, and hope for the best.
In a narrow sense, that strategy has been wildly successful, as those three blue boxes can attest. In 2025, 457 players saw at least 100 pitches within those boxes. Wood’s 50% swing rate ranked 376th, meaning he took way more called strikes than the average player. When he did swing, his 28.7% whiff rate was tied for 426th place, meaning that he ended up with way more swinging strikes than the average player. When Wood put the ball in play, he was more successful than the average player, because of course he was. Even though that’s the spot where he has his lowest bat speed, lowest exit velocity, and lowest launch angle, he still hits the ball so hard that it can’t help but find grass. He ran a .418 wOBACON on those pitches. But that’s not enough to mitigate all those extra strikes.
In a broader sense, that plan has its limits. Aiming for the corner against a player as patient as Wood means that when you miss, you’ve got a higher chance of missing the zone entirely, and Wood is so patient that he’ll make you pay for it. Once you’re behind, you have to hit the heart of the zone. More importantly, this is something of a desperation move. For years now, the trend across the league has been toward throwing the ball right over the middle and trusting your stuff to do the rest. The fear of grooving a pitch to Wood is driving pitchers toward an older, less successful game plan. Wood is bad at handling that pitch, but so is every hitter on earth. He’s seeing so many pitches there because against a hitter like him, all the options are suboptimal. Wood may not get to the next level as a hitter until he can find a way to cover more of the strike zone, but he’s young and he’s still learning. He may well get there. In the meantime, he’s still striking fear into the hearts of pitchers, and they’re doing their best to stay away from him.
Davy Andrews is a Brooklyn-based musician and a writer at FanGraphs. He can be found on Bluesky @davyandrewsdavy.bsky.social.
Cacophonous silence in the comments. You did it Davy! You wrote an article to which nothing can be said!
This seems like the kind of problem that doesn’t really hurt a guy over the course of a regular season but can haunt him in October. I hope we get to find out one day, he’s a cool player.