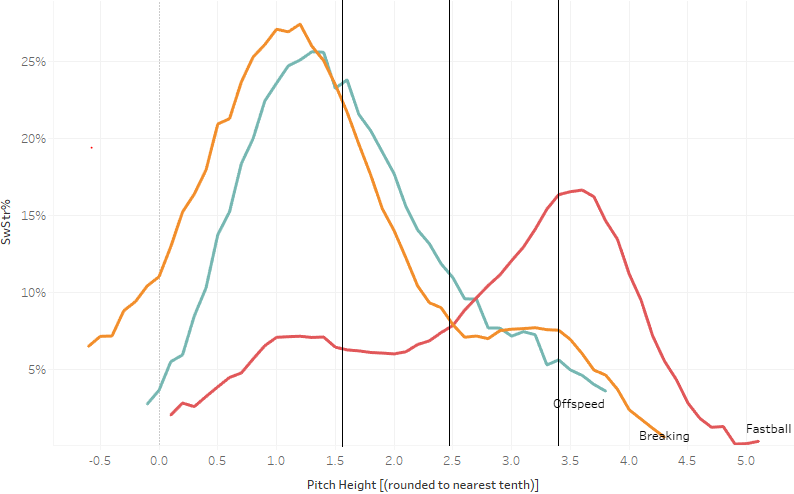
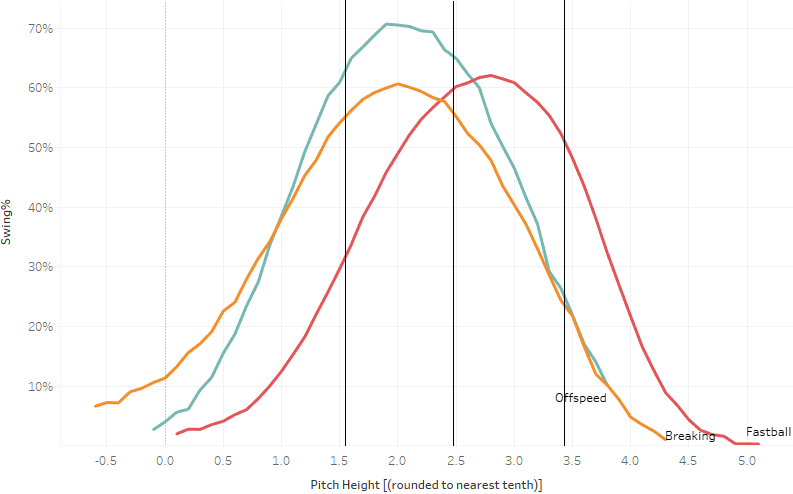
Do Successful Steals Apply Measurable Pressure?
Consider the plight of the base stealer. In the 1980s, their role was sacrosanct. Get on base first, then cause havoc. For fans of speed and baserunning, it was a veritable golden age. Rickey Henderson and Vince Coleman each stole 100 bases in three separate seasons. Since 1980, the 13 top seasons in terms of stolen bases per plate appearance were 1980 through 1992.
Alas, the scurrilous forces of math and efficiency conspired to dethrone the stolen base. As it turns out, advancing one base is less good than creating an out is bad. It’s bad enough, in fact, that you need about three successful stolen bases to make up for the downside of getting caught once. The very best thieves managed that level of efficiency, but in aggregate, the league only crested a 70% success rate once from 1980 to 1992. Steals simply weren’t advancing teams’ goal of scoring as many runs as possible.
For a time, there was a reasonable counter-argument: what if attempting a stolen base has positive value that isn’t solely contained in reaching second base? Perhaps the pitcher has steals on the brain, or the defense loses its cohesion while attempting to cover the base for a throw. It doesn’t need to add much edge to make the math add up.
In 2007, the authors of The Book took up this question. They found a large advantage to batters when a runner was on first — exactly what proponents of steals suggested. There was a big problem, however. That advantage was for all runners on first base. The faster the runner, the smaller the advantage. In addition, actually attempting a steal carried a huge hit to the batter, more than enough to offset the advantage of having a runner on base. Read the rest of this entry »