2026 ZiPS Projections: Atlanta Braves
For the 22nd consecutive season, the ZiPS projection system is unleashing a full set of prognostications. For more information on the ZiPS projections, please consult this year’s introduction, as well as MLB’s glossary entry. The team order is selected by lot, and the next team up is the Atlanta Braves.
Batters
Remember how 2024 was a major disappointment for the Atlanta Braves? Well, Father Time apparently took umbrage at that description being applied to an 89-win team that at least made the playoffs, and proceeded to have his beer held as he cooked up something really disappointing in his workshop. The Braves finished with a 76-86 record, the team’s worst showing in a season where it was actually considered a viable contender coming into Opening Day since 2008. Now they hope to put things back together with more or less the same core talent.
Just looking at our depth chart, you’d feel pretty good about the Braves, except for a couple things: They look a bit worse at (almost) every position than they did at this time last year, and we’re getting those WAR numbers with quite a lot of the starters projected for at least 600 plate appearances. The first is a problem because a team with slightly better projections just won 76 games, and the second is worrisome because ZiPS is quite meh on Atlanta’s offensive talent once you get past the team’s impressive first-tier players.
The one place where the Braves did get a projection boost is at catcher, with Drake Baldwin a lot more established than he was coming into 2025. The position didn’t disappoint this season, and there’s no reason for particular worry here. Holding steady is Matt Olson, who more than pulled his weight in his fourth consecutive ironman season. His 2025 paled next to 2023’s 54-homer campaign, likely Olson’s high-water mark, but it represented a nice recovery from a down 2024.
Elsewhere, there are questions. Austin Riley missed significant time to injury, and for the third consecutive season, he shed a good chunk of his wRC+. Ronald Acuña Jr. was his usual terrific self when healthy, but after being plagued by Achilles issues, he appears to be running out of parts in his legs that haven’t been injured. Michael Harris II suddenly hit like a Double-A player for months, and though he made up some of the loss with a hot July and August, you have to have questions about a major leaguer who can go a half-season with a .234 on-base percentage. I’m also not sure that Ozzie Albies is even good anymore, which is a major bummer, as he’s now only a couple of years from hitting free agency and otherwise having the opportunity to make up for one of the worst pre-free agency contracts ever signed by a good player.
Help is unlikely to come from the minors. Atlanta has developed an impressive number of position players, but until/unless the 2025 draftees succeed, Baldwin might be the last short-term boost from within for a bit. And while the Braves aren’t cheap in the sense that teams like the Rays or Marlins are, the organization isn’t known for being super aggressive in free agency.
In short: If the Braves get a bit of good fortune for a change, this could be a really good lineup, but there’s a lot that could easily go very wrong.
Pitchers
The problem with the starting lineup’s projections repeats here, especially in the rotation: There are a lot of good projections, but they’re mostly a bit worse than they were last year. Unfortunately, pitchers being pitchers, I have less confidence in the rotation staying healthy than I do the lineup.
I’m certainly hopeful about Chris Sale, whose late-career mini-comeback has put him in plausible Hall of Fame territory, at least for me. On the plus side, his rib cage injury, like the bicycle-aided broken wrist in 2022, wasn’t a recurrence of his prior elbow problems, so I’m cautiously optimistic here. But he’s also going to be 37, an age where decline becomes a serious year-to-year concern for pitchers.
Both ZiPS and I are relatively bullish on Spencer Schwellenbach coming back from the stress fracture in his elbow, even if he has to give back some velocity to take some pressure off things. Reynaldo López’s shoulder showed no structural damage, but baseball’s medical wizards have become adept at fixing elbows quicker than shoulders, so caution is warranted there. I personally have no idea what Spencer Strider is now, as he’s lost a lot of velocity and his ability to get whiffs inside the strike zone is diminished.
The good news is that ZiPS sees Atlanta’s rotation as having better emergency options than the lineup. Bryce Elder and Hurston Waldrep are reasonable fifth starter options, and the computer thinks JR Ritchie and Lucas Braun could fill-in where needed without it being a major disaster.
ZiPS projects the bullpen to be competently average, and while nobody is forecast to be a dominant arm, the numbers don’t start looking worrisome until you get to the sixth or seventh relievers, which is true of most teams this early in the offseason. ZiPS sees Joel Payamps as a decent addition who adds some heft to the ‘pen. I expect a few moves to be made here, though it’s unlikely to be anything that would push Atlanta into being a top tier bullpen.
When you assume that a lot of injuries will inevitably happen, the Braves look like an 84-88 win team (or somewhere thereabouts) depending on who the healthy guys are. That’s better than last year’s finish, but still kind of a disappointment. Uh oh, maybe I should avoid using that word again!
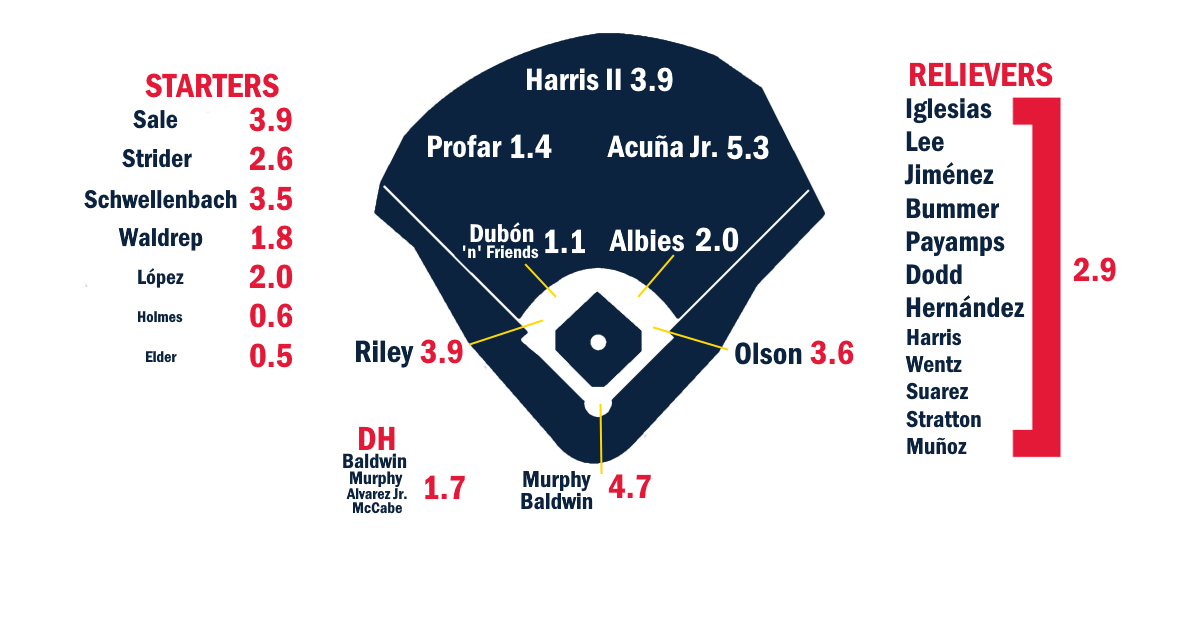
Ballpark graphic courtesy Eephus League. Depth charts constructed by way of those listed here. Size of player names is very roughly proportional to Depth Chart playing time. The final team projections may differ considerably from our Depth Chart playing time.
| Player | B | Age | PO | PA | AB | R | H | 2B | 3B | HR | RBI | BB | SO | SB | CS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ronald Acuña Jr. | R | 28 | RF | 529 | 444 | 101 | 127 | 21 | 1 | 27 | 71 | 78 | 110 | 24 | 5 |
| Michael Harris II | L | 25 | CF | 609 | 574 | 74 | 158 | 29 | 4 | 22 | 80 | 24 | 118 | 19 | 5 |
| Drake Baldwin | L | 25 | C | 485 | 434 | 56 | 115 | 23 | 1 | 21 | 71 | 45 | 92 | 0 | 0 |
| Matt Olson | L | 32 | 1B | 661 | 575 | 86 | 144 | 33 | 1 | 30 | 91 | 77 | 159 | 1 | 0 |
| Austin Riley | R | 29 | 3B | 539 | 488 | 72 | 128 | 26 | 2 | 25 | 72 | 40 | 138 | 2 | 1 |
| Sean Murphy | R | 31 | C | 367 | 321 | 41 | 72 | 15 | 0 | 17 | 47 | 35 | 99 | 0 | 0 |
| Marcell Ozuna | R | 35 | DH | 566 | 487 | 66 | 121 | 21 | 0 | 25 | 76 | 72 | 139 | 0 | 0 |
| Ha-Seong Kim | R | 30 | SS | 441 | 385 | 51 | 94 | 16 | 1 | 9 | 44 | 46 | 77 | 17 | 4 |
| Ozzie Albies | B | 29 | 2B | 601 | 545 | 73 | 136 | 26 | 2 | 18 | 70 | 45 | 87 | 11 | 3 |
| Jesús Bastidas | R | 27 | 3B | 546 | 491 | 67 | 112 | 25 | 2 | 14 | 70 | 36 | 148 | 9 | 3 |
| Brett Wisely | L | 27 | 2B | 433 | 387 | 52 | 94 | 20 | 2 | 9 | 48 | 36 | 98 | 8 | 3 |
| Nacho Alvarez Jr. | R | 23 | 3B | 437 | 389 | 44 | 92 | 17 | 0 | 6 | 41 | 36 | 92 | 5 | 2 |
| Eli White | R | 32 | RF | 308 | 283 | 44 | 68 | 9 | 2 | 8 | 35 | 19 | 85 | 13 | 2 |
| Jurickson Profar | B | 33 | LF | 501 | 433 | 64 | 109 | 23 | 1 | 14 | 56 | 57 | 79 | 7 | 1 |
| Charles Leblanc | R | 30 | 3B | 359 | 315 | 38 | 74 | 13 | 1 | 8 | 43 | 38 | 104 | 3 | 2 |
| Brewer Hicklen | R | 30 | RF | 410 | 362 | 54 | 77 | 15 | 2 | 14 | 55 | 35 | 144 | 18 | 2 |
| Alex Verdugo | L | 30 | LF | 469 | 426 | 57 | 107 | 24 | 1 | 9 | 44 | 35 | 70 | 3 | 1 |
| Conner Capel | L | 29 | RF | 405 | 366 | 39 | 81 | 13 | 3 | 9 | 41 | 35 | 96 | 13 | 4 |
| Luke Waddell | L | 27 | 2B | 456 | 406 | 43 | 95 | 18 | 1 | 2 | 36 | 38 | 70 | 6 | 3 |
| Mauricio Dubón | R | 31 | 2B | 402 | 375 | 47 | 95 | 19 | 1 | 6 | 37 | 20 | 47 | 3 | 1 |
| Jake Marisnick | R | 35 | CF | 186 | 168 | 21 | 36 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 21 | 12 | 60 | 5 | 2 |
| Jonathan Ornelas | R | 26 | SS | 477 | 432 | 47 | 94 | 11 | 2 | 7 | 44 | 36 | 132 | 7 | 3 |
| Michael Siani | L | 26 | CF | 458 | 406 | 53 | 83 | 12 | 3 | 6 | 38 | 40 | 126 | 19 | 5 |
| Cody Milligan | L | 27 | LF | 409 | 364 | 46 | 81 | 15 | 3 | 3 | 33 | 36 | 118 | 15 | 4 |
| Jair Camargo | R | 26 | C | 301 | 282 | 27 | 59 | 11 | 1 | 8 | 33 | 15 | 113 | 2 | 1 |
| Vidal Bruján | B | 28 | 3B | 296 | 268 | 36 | 61 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 26 | 21 | 62 | 10 | 7 |
| David McCabe | B | 26 | 3B | 503 | 450 | 48 | 105 | 21 | 1 | 11 | 50 | 48 | 132 | 2 | 1 |
| Eddy Alvarez | L | 36 | CF | 306 | 262 | 38 | 54 | 12 | 1 | 6 | 32 | 27 | 88 | 9 | 4 |
| José Azocar | R | 30 | CF | 336 | 312 | 41 | 75 | 13 | 2 | 4 | 30 | 17 | 75 | 15 | 6 |
| Chuckie Robinson | R | 31 | C | 315 | 291 | 31 | 65 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 29 | 17 | 89 | 1 | 1 |
| Jarred Kelenic | L | 26 | CF | 466 | 426 | 49 | 98 | 22 | 2 | 12 | 49 | 37 | 143 | 9 | 5 |
| Jim Jarvis | L | 25 | SS | 406 | 374 | 52 | 85 | 19 | 1 | 2 | 37 | 22 | 65 | 8 | 4 |
| Austin Nola | R | 36 | C | 187 | 165 | 17 | 36 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 15 | 14 | 36 | 0 | 0 |
| Garrett Cooper | R | 35 | 1B | 315 | 286 | 24 | 66 | 14 | 1 | 8 | 35 | 23 | 92 | 1 | 0 |
| Jose Devers | L | 26 | 2B | 285 | 262 | 33 | 61 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 28 | 16 | 51 | 2 | 1 |
| Chandler Seagle | R | 30 | C | 197 | 183 | 14 | 32 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 8 | 75 | 1 | 1 |
| David Fletcher | R | 32 | 3B | 341 | 320 | 26 | 70 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 27 | 16 | 49 | 4 | 1 |
| E.J. Exposito | R | 25 | 3B | 431 | 396 | 44 | 82 | 15 | 2 | 11 | 46 | 25 | 133 | 8 | 3 |
| Sandy León | B | 37 | C | 211 | 185 | 15 | 30 | 5 | 0 | 6 | 20 | 19 | 77 | 1 | 0 |
| Chadwick Tromp | R | 31 | C | 270 | 250 | 23 | 51 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 24 | 18 | 73 | 1 | 0 |
| Keshawn Ogans | R | 24 | 3B | 363 | 328 | 29 | 72 | 13 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 24 | 73 | 5 | 5 |
| Luke Williams | R | 29 | 3B | 301 | 276 | 33 | 56 | 12 | 1 | 5 | 30 | 20 | 93 | 18 | 3 |
| John Gil | R | 20 | SS | 487 | 443 | 59 | 95 | 19 | 1 | 5 | 40 | 36 | 97 | 22 | 7 |
| Dylan Shockley | R | 29 | C | 149 | 132 | 11 | 22 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 11 | 66 | 0 | 0 |
| Kobe Kato | L | 27 | 2B | 236 | 207 | 22 | 39 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 19 | 25 | 73 | 10 | 3 |
| Matthew Batten | R | 31 | 1B | 447 | 407 | 42 | 81 | 16 | 1 | 8 | 41 | 33 | 125 | 11 | 2 |
| Will Verdung | R | 23 | 1B | 330 | 298 | 27 | 65 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 22 | 27 | 72 | 3 | 3 |
| Ambioris Tavarez | R | 22 | 2B | 435 | 393 | 40 | 77 | 10 | 1 | 6 | 36 | 33 | 183 | 11 | 4 |
| Cade Bunnell | L | 29 | 1B | 343 | 305 | 26 | 54 | 11 | 1 | 7 | 31 | 35 | 154 | 3 | 1 |
| Ethan Workinger | R | 24 | RF | 503 | 466 | 52 | 104 | 19 | 2 | 12 | 52 | 32 | 114 | 6 | 4 |
| Drew Compton | B | 25 | 1B | 430 | 395 | 35 | 90 | 19 | 1 | 4 | 35 | 32 | 126 | 1 | 0 |
| Stephen Paolini | L | 25 | RF | 311 | 281 | 31 | 54 | 10 | 1 | 5 | 27 | 24 | 119 | 11 | 3 |
| Patrick Clohisy | L | 24 | CF | 551 | 507 | 57 | 117 | 19 | 3 | 5 | 49 | 35 | 123 | 36 | 10 |
| Joe Olsavsky | R | 24 | 1B | 314 | 275 | 26 | 52 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 31 | 23 | 82 | 3 | 1 |
| Adam Zebrowski | R | 25 | C | 380 | 350 | 31 | 69 | 12 | 1 | 8 | 37 | 24 | 128 | 2 | 1 |
| Justin Janas | L | 25 | RF | 395 | 361 | 35 | 83 | 13 | 1 | 4 | 40 | 18 | 83 | 5 | 2 |
| Kevin Kilpatrick Jr. | R | 25 | CF | 459 | 420 | 51 | 86 | 14 | 3 | 3 | 36 | 31 | 132 | 17 | 6 |
| Mac Guscette | R | 24 | C | 268 | 244 | 16 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 21 | 16 | 52 | 0 | 2 |
| Carlos Arroyo | R | 24 | 2B | 160 | 148 | 10 | 24 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 7 | 59 | 2 | 1 |
| Geraldo Quintero | B | 24 | LF | 434 | 388 | 48 | 82 | 12 | 3 | 6 | 41 | 37 | 102 | 18 | 10 |
| Tyler Tolve | L | 25 | C | 246 | 229 | 22 | 42 | 9 | 0 | 6 | 24 | 12 | 108 | 1 | 0 |
| Jake Steels | R | 24 | LF | 235 | 209 | 18 | 36 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 17 | 16 | 57 | 1 | 2 |
| Lizandro Espinoza | R | 23 | SS | 431 | 396 | 48 | 72 | 14 | 2 | 10 | 42 | 23 | 147 | 10 | 7 |
| Cal Conley | B | 26 | SS | 528 | 486 | 54 | 102 | 15 | 3 | 3 | 39 | 29 | 121 | 16 | 6 |
| Colby Jones | R | 22 | 2B | 498 | 449 | 55 | 88 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 32 | 39 | 132 | 27 | 10 |
| Isaiah Drake | L | 20 | CF | 480 | 444 | 42 | 95 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 36 | 31 | 144 | 19 | 7 |
| Mason Guerra | R | 23 | 1B | 393 | 355 | 32 | 64 | 9 | 1 | 10 | 38 | 32 | 124 | 0 | 0 |
| Bryson Horne | L | 27 | 1B | 337 | 317 | 25 | 63 | 11 | 1 | 7 | 31 | 16 | 119 | 2 | 1 |
| Jace Grady | B | 25 | RF | 301 | 274 | 23 | 49 | 11 | 0 | 3 | 22 | 22 | 88 | 4 | 3 |
| Player | PA | BA | OBP | SLG | OPS+ | ISO | BABIP | Def | WAR | wOBA | 3YOPS+ | RC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ronald Acuña Jr. | 529 | .286 | .399 | .520 | 157 | .234 | .326 | -4 | 4.5 | .395 | 155 | 99 |
| Michael Harris II | 609 | .275 | .308 | .455 | 112 | .180 | .313 | 7 | 3.8 | .326 | 112 | 86 |
| Drake Baldwin | 485 | .265 | .340 | .468 | 125 | .203 | .293 | 0 | 3.7 | .349 | 125 | 69 |
| Matt Olson | 661 | .250 | .342 | .468 | 126 | .218 | .295 | 4 | 3.4 | .348 | 119 | 92 |
| Austin Riley | 539 | .262 | .325 | .477 | 123 | .215 | .317 | -1 | 3.2 | .343 | 119 | 76 |
| Sean Murphy | 367 | .224 | .316 | .430 | 108 | .206 | .268 | 5 | 2.6 | .324 | 103 | 44 |
| Marcell Ozuna | 566 | .248 | .346 | .446 | 122 | .198 | .297 | 0 | 2.4 | .344 | 113 | 75 |
| Ha-Seong Kim | 441 | .244 | .328 | .361 | 95 | .117 | .284 | 3 | 2.1 | .306 | 92 | 51 |
| Ozzie Albies | 601 | .250 | .309 | .404 | 99 | .154 | .268 | -2 | 1.9 | .310 | 98 | 72 |
| Jesús Bastidas | 546 | .228 | .299 | .373 | 88 | .145 | .298 | 4 | 1.6 | .295 | 88 | 58 |
| Brett Wisely | 433 | .243 | .310 | .375 | 92 | .132 | .304 | 4 | 1.6 | .300 | 90 | 48 |
| Nacho Alvarez Jr. | 437 | .237 | .317 | .326 | 82 | .089 | .296 | 8 | 1.5 | .290 | 85 | 42 |
| Eli White | 308 | .240 | .296 | .371 | 87 | .131 | .316 | 8 | 1.1 | .292 | 84 | 35 |
| Jurickson Profar | 501 | .252 | .346 | .406 | 112 | .154 | .279 | -7 | 1.1 | .331 | 109 | 63 |
| Charles Leblanc | 359 | .235 | .324 | .359 | 93 | .124 | .325 | 0 | 1.0 | .304 | 92 | 38 |
| Brewer Hicklen | 410 | .213 | .298 | .381 | 90 | .169 | .309 | 3 | 0.9 | .298 | 89 | 46 |
| Alex Verdugo | 469 | .251 | .310 | .376 | 92 | .125 | .282 | 2 | 0.7 | .301 | 92 | 51 |
| Conner Capel | 405 | .221 | .291 | .347 | 79 | .126 | .276 | 7 | 0.6 | .282 | 78 | 41 |
| Luke Waddell | 456 | .234 | .304 | .298 | 71 | .064 | .278 | 5 | 0.6 | .272 | 73 | 39 |
| Mauricio Dubón | 402 | .253 | .293 | .357 | 82 | .104 | .276 | 0 | 0.6 | .284 | 82 | 40 |
| Jake Marisnick | 186 | .214 | .281 | .369 | 82 | .155 | .301 | 1 | 0.4 | .285 | 74 | 19 |
| Jonathan Ornelas | 477 | .218 | .286 | .301 | 66 | .083 | .297 | 3 | 0.4 | .262 | 69 | 40 |
| Michael Siani | 458 | .204 | .279 | .293 | 62 | .089 | .281 | 7 | 0.4 | .258 | 65 | 39 |
| Cody Milligan | 409 | .223 | .297 | .305 | 71 | .082 | .321 | 8 | 0.3 | .271 | 71 | 38 |
| Jair Camargo | 301 | .209 | .256 | .340 | 67 | .131 | .317 | 2 | 0.3 | .260 | 73 | 25 |
| Vidal Bruján | 296 | .228 | .292 | .321 | 73 | .093 | .282 | 3 | 0.3 | .272 | 75 | 30 |
| David McCabe | 503 | .233 | .306 | .358 | 87 | .125 | .306 | -7 | 0.2 | .293 | 88 | 50 |
| Eddy Alvarez | 306 | .206 | .300 | .328 | 78 | .122 | .286 | -1 | 0.2 | .283 | 75 | 29 |
| José Azocar | 336 | .240 | .284 | .333 | 74 | .093 | .305 | 1 | 0.2 | .272 | 76 | 35 |
| Chuckie Robinson | 315 | .223 | .274 | .309 | 64 | .086 | .305 | 1 | 0.1 | .259 | 62 | 25 |
| Jarred Kelenic | 466 | .230 | .292 | .376 | 87 | .146 | .317 | -7 | 0.1 | .291 | 88 | 51 |
| Jim Jarvis | 406 | .227 | .283 | .299 | 65 | .072 | .270 | 2 | 0.1 | .260 | 68 | 35 |
| Austin Nola | 187 | .218 | .284 | .309 | 68 | .091 | .262 | -2 | 0.0 | .263 | 67 | 14 |
| Garrett Cooper | 315 | .231 | .295 | .371 | 87 | .140 | .312 | 1 | 0.0 | .292 | 82 | 32 |
| Jose Devers | 285 | .233 | .285 | .328 | 73 | .095 | .279 | -1 | 0.0 | .271 | 72 | 25 |
| Chandler Seagle | 197 | .175 | .221 | .235 | 29 | .060 | .290 | 7 | -0.1 | .205 | 28 | 10 |
| David Fletcher | 341 | .219 | .259 | .272 | 50 | .053 | .253 | 8 | -0.1 | .237 | 50 | 24 |
| E.J. Exposito | 431 | .207 | .260 | .338 | 67 | .131 | .282 | 2 | -0.1 | .262 | 71 | 38 |
| Sandy León | 211 | .162 | .246 | .286 | 50 | .124 | .235 | 1 | -0.1 | .241 | 44 | 13 |
| Chadwick Tromp | 270 | .204 | .256 | .316 | 60 | .112 | .263 | 0 | -0.1 | .252 | 58 | 20 |
| Keshawn Ogans | 363 | .220 | .287 | .284 | 62 | .064 | .277 | 2 | -0.2 | .259 | 63 | 30 |
| Luke Williams | 301 | .203 | .259 | .308 | 59 | .105 | .287 | 1 | -0.2 | .251 | 59 | 27 |
| John Gil | 487 | .214 | .278 | .296 | 62 | .082 | .264 | -3 | -0.2 | .258 | 68 | 44 |
| Dylan Shockley | 149 | .167 | .250 | .205 | 31 | .038 | .323 | 2 | -0.3 | .215 | 29 | 7 |
| Kobe Kato | 236 | .188 | .284 | .275 | 59 | .087 | .275 | -2 | -0.3 | .257 | 60 | 19 |
| Matthew Batten | 447 | .199 | .263 | .302 | 59 | .103 | .266 | 10 | -0.4 | .252 | 58 | 35 |
| Will Verdung | 330 | .218 | .285 | .262 | 56 | .044 | .288 | 8 | -0.5 | .248 | 58 | 24 |
| Ambioris Tavarez | 435 | .196 | .269 | .272 | 54 | .076 | .348 | 2 | -0.6 | .245 | 59 | 33 |
| Cade Bunnell | 343 | .177 | .265 | .289 | 57 | .112 | .326 | 6 | -0.6 | .251 | 56 | 24 |
| Ethan Workinger | 503 | .223 | .276 | .350 | 75 | .127 | .271 | 0 | -0.6 | .275 | 79 | 48 |
| Drew Compton | 430 | .228 | .286 | .311 | 69 | .083 | .325 | 3 | -0.7 | .265 | 71 | 35 |
| Stephen Paolini | 311 | .192 | .264 | .288 | 56 | .096 | .312 | 3 | -0.7 | .248 | 60 | 25 |
| Patrick Clohisy | 551 | .231 | .287 | .310 | 69 | .079 | .296 | -8 | -0.7 | .266 | 73 | 57 |
| Joe Olsavsky | 314 | .189 | .290 | .251 | 55 | .062 | .262 | 3 | -0.8 | .254 | 59 | 21 |
| Adam Zebrowski | 380 | .197 | .255 | .306 | 58 | .109 | .285 | -5 | -0.8 | .249 | 65 | 28 |
| Justin Janas | 395 | .230 | .291 | .305 | 69 | .075 | .288 | -1 | -0.8 | .268 | 71 | 34 |
| Kevin Kilpatrick Jr. | 459 | .205 | .268 | .274 | 54 | .069 | .291 | 1 | -0.8 | .245 | 58 | 37 |
| Mac Guscette | 268 | .184 | .246 | .262 | 44 | .078 | .226 | -2 | -0.9 | .229 | 46 | 17 |
| Carlos Arroyo | 160 | .162 | .219 | .216 | 24 | .054 | .261 | -1 | -1.0 | .199 | 32 | 8 |
| Geraldo Quintero | 434 | .211 | .290 | .304 | 68 | .093 | .271 | -2 | -1.0 | .268 | 72 | 42 |
| Tyler Tolve | 246 | .183 | .232 | .301 | 49 | .118 | .313 | -5 | -1.0 | .235 | 53 | 16 |
| Jake Steels | 235 | .172 | .249 | .215 | 33 | .043 | .232 | 4 | -1.1 | .217 | 33 | 12 |
| Lizandro Espinoza | 431 | .182 | .234 | .303 | 50 | .121 | .259 | -2 | -1.1 | .237 | 56 | 33 |
| Cal Conley | 528 | .210 | .259 | .272 | 50 | .062 | .273 | -2 | -1.2 | .238 | 51 | 40 |
| Colby Jones | 498 | .196 | .269 | .227 | 42 | .031 | .275 | 3 | -1.2 | .230 | 46 | 37 |
| Isaiah Drake | 480 | .214 | .267 | .286 | 56 | .072 | .305 | -5 | -1.3 | .247 | 59 | 41 |
| Mason Guerra | 393 | .180 | .254 | .296 | 55 | .116 | .244 | 1 | -1.4 | .247 | 61 | 27 |
| Bryson Horne | 337 | .199 | .240 | .306 | 53 | .107 | .293 | 0 | -1.6 | .239 | 56 | 24 |
| Jace Grady | 301 | .179 | .243 | .252 | 40 | .073 | .251 | -2 | -1.9 | .224 | 41 | 19 |
| Player | Hit Comp 1 | Hit Comp 2 | Hit Comp 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ronald Acuña Jr. | Christian Yelich | Mike Trout | Rickey Henderson |
| Michael Harris II | Willie Davis | Roy Weatherly | Jose Cardenal |
| Drake Baldwin | Bill Freehan | John Orsino | Sherm Lollar |
| Matt Olson | Carlos Delgado | Mark Teixeira | Travis Hafner |
| Austin Riley | Mike Shannon | Pinky Higgins | Hector Lopez |
| Sean Murphy | Jim Pagliaroni | John Buck | Geovany Soto |
| Marcell Ozuna | Boog Powell | Frank Thomas | Jason Giambi |
| Ha-Seong Kim | Sparky Adams | Dick Howser | Eric Young Sr. |
| Ozzie Albies | Frank Bolling | Todd Walker | John Castino |
| Jesús Bastidas | Casey Blake | Stan Jok | Jeff Moronko |
| Brett Wisely | La Rue Washington | Richard Littleton | Jimmy Stewart |
| Nacho Alvarez Jr. | Matt Erickson | Dave Cripe | Freddy Zamora |
| Eli White | Mark Little | Peter Bourjos | Jason Repko |
| Jurickson Profar | Will Clark | Matt Lawton | Rusty Greer |
| Charles Leblanc | Danny Worth | Zach Lutz 루츠 | Oscar Grimes |
| Brewer Hicklen | Brian O’Grady | Jose Vidal | Jeremy Hazelbaker |
| Alex Verdugo | Jason Krizan | Harry Schwegman | Dario Pizzano |
| Conner Capel | Jeff Salazar | Bruce Dostal | Guy Rose |
| Luke Waddell | Brian David | J.D. Pulfer | Casey Wise |
| Mauricio Dubón | Rennie Stennett | Ildemaro Vargas | Mickey McGuire |
| Jake Marisnick | Dewayne Wise | Clay Bellinger | John Shelby |
| Jonathan Ornelas | Mark Belanger | Jamie Athas | Willie Lozado |
| Michael Siani | George McPherson | Mike Mesh | Tony Russell |
| Cody Milligan | Adam Heisler | Roberto Caro | Jeff Duncan |
| Jair Camargo | Randall Schafer | Steve Hagins | Chris Wallace |
| Vidal Bruján | Rosell Herrera | Larry Eckenrode | Sergio Ferrer |
| David McCabe | Matt Davis | Chris Saunders | Rick Albert |
| Eddy Alvarez | Andres Torres | Shawn Gilbert | Michael Tucker |
| José Azocar | Rudy Rufer | Wynton Bernard | Joe Simpson |
| Chuckie Robinson | Reynaldo Oliver | Donald Griffin | Pat Tomkinson |
| Jarred Kelenic | Mike Gerber | Kirk Nieuwenhuis | Gary Woods |
| Jim Jarvis | Rich Almanzar | Melvin Dorta | Julius Matos |
| Austin Nola | Billy Shantz | Gary Bennett | John DeBerry |
| Garrett Cooper | Wil Cordero | Tom Wilson | Joseph Christian |
| Jose Devers | Christian Stringer | Steve Hine | Evel Bastida |
| Chandler Seagle | Donny Lucy | Tom Gregorio | John Nathans |
| David Fletcher | Billy DeMars | Jose Lind | Jerry Dybzinski |
| E.J. Exposito | Robert Watson | Dan Uggla | Jeff Eure |
| Sandy León | Louis Heyman | Ed Sadowski | Ebba St. Claire |
| Chadwick Tromp | A.J. Hinch | Matt Pagnozzi | Larry Owen |
| Keshawn Ogans | Tony Garcia | Wayne Edwards | Art Cleary |
| Luke Williams | Chris Owings | Matt Hagen | Kevin Connacher |
| John Gil | Vic Gutierrez | Omar Infante | Rob Valido |
| Dylan Shockley | Dave Ullery | Steve Lomasney | Ryan Bennett |
| Kobe Kato | Scot Pyle | Chick Fewster | Billy Bone |
| Matthew Batten | Alex Garbowski | Kimera Bartee | John Massarelli |
| Will Verdung | Dave Hoenstine | Dan Robinson | Vince Palyan |
| Ambioris Tavarez | Mark Simmons | Joey Millis | Angelo Nunley |
| Cade Bunnell | John Curl | Mike Wishnevski | Eric Crozier |
| Ethan Workinger | Bob Zupcic | Motorboat Jones | Luis Montanez |
| Drew Compton | Rhyne Hughes | Juan Figueroa | Jason Turner |
| Stephen Paolini | Grant Steer | Travis Becktel | Bo Williams |
| Patrick Clohisy | Tom Goodwin | Gene Kingsale | Ryan Knox |
| Joe Olsavsky | Isaias Nunez | Jalen Washington | Brandon Green |
| Adam Zebrowski | Ronald Jacobs | Ray Roman | Jerry Grote |
| Justin Janas | Ernie De La Trinidad | Ryan Fleming | Marcelo Juarez |
| Kevin Kilpatrick Jr. | Maiko Loyola | Victor Horacio | Alonzo Harris |
| Mac Guscette | Danny Lehmann | Matt Tupman | Carlos Paulino |
| Carlos Arroyo | Michael Wilbins | Mike Rizzo | Welfrin Mateo |
| Geraldo Quintero | Ryan Rogowski | Lucas Montero | Francisco Soriano |
| Tyler Tolve | James Handley | Andy Hall | Jacob Wallis |
| Jake Steels | Leonardo Reyes | Arthur Wilson | Glen Spencer |
| Lizandro Espinoza | Kelly Dransfeldt | Ramon Araujo | Brandon Warriax |
| Cal Conley | Wilmy Caceres | Derek Wathan | Craig Robinson |
| Colby Jones | D.J. Burt | Pat Listach | Pete Maropis |
| Isaiah Drake | Kevin Kiermaier | Jeramie Simpson | Josh Womack |
| Mason Guerra | Pat Adams | Bobby Jack | Tom Hardgrove |
| Bryson Horne | Tim Pahuta | Ben Waldrip | Chris Serritella |
| Jace Grady | Doug Shields | Mike Epping | Billy Argo |
| Player | 80th BA | 80th OBP | 80th SLG | 80th OPS+ | 80th WAR | 20th BA | 20th OBP | 20th SLG | 20th OPS+ | 20th WAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ronald Acuña Jr. | .312 | .427 | .590 | 180 | 5.8 | .256 | .369 | .475 | 137 | 3.1 |
| Michael Harris II | .303 | .334 | .503 | 130 | 5.3 | .249 | .283 | .402 | 91 | 2.2 |
| Drake Baldwin | .295 | .369 | .520 | 148 | 5.1 | .241 | .313 | .415 | 105 | 2.5 |
| Matt Olson | .276 | .363 | .525 | 146 | 4.9 | .224 | .316 | .423 | 108 | 2.0 |
| Austin Riley | .288 | .352 | .543 | 145 | 4.6 | .238 | .302 | .431 | 105 | 2.0 |
| Sean Murphy | .247 | .339 | .485 | 129 | 3.6 | .197 | .286 | .372 | 86 | 1.7 |
| Marcell Ozuna | .274 | .372 | .504 | 142 | 3.7 | .224 | .324 | .395 | 104 | 1.2 |
| Ha-Seong Kim | .271 | .354 | .404 | 113 | 3.1 | .220 | .304 | .319 | 78 | 1.2 |
| Ozzie Albies | .275 | .335 | .450 | 116 | 3.2 | .226 | .286 | .364 | 82 | 0.6 |
| Jesús Bastidas | .252 | .322 | .421 | 106 | 2.8 | .201 | .272 | .321 | 68 | 0.3 |
| Brett Wisely | .266 | .336 | .416 | 108 | 2.4 | .216 | .285 | .331 | 74 | 0.6 |
| Nacho Alvarez Jr. | .262 | .345 | .360 | 98 | 2.4 | .208 | .293 | .287 | 65 | 0.6 |
| Eli White | .274 | .322 | .427 | 107 | 1.9 | .210 | .264 | .320 | 67 | 0.3 |
| Jurickson Profar | .279 | .372 | .449 | 128 | 2.1 | .226 | .319 | .360 | 92 | -0.2 |
| Charles Leblanc | .260 | .352 | .408 | 114 | 1.9 | .205 | .295 | .314 | 74 | 0.1 |
| Brewer Hicklen | .241 | .325 | .435 | 112 | 2.0 | .185 | .272 | .324 | 68 | -0.1 |
| Alex Verdugo | .281 | .339 | .426 | 114 | 1.9 | .229 | .284 | .338 | 76 | -0.3 |
| Conner Capel | .247 | .320 | .400 | 101 | 1.6 | .197 | .263 | .307 | 61 | -0.4 |
| Luke Waddell | .262 | .331 | .329 | 88 | 1.5 | .208 | .277 | .259 | 54 | -0.4 |
| Mauricio Dubón | .281 | .317 | .401 | 101 | 1.5 | .228 | .266 | .319 | 65 | -0.3 |
| Jake Marisnick | .246 | .310 | .427 | 102 | 0.9 | .185 | .250 | .310 | 57 | -0.1 |
| Jonathan Ornelas | .242 | .312 | .341 | 85 | 1.4 | .189 | .259 | .264 | 49 | -0.7 |
| Michael Siani | .234 | .305 | .338 | 81 | 1.6 | .177 | .251 | .259 | 47 | -0.4 |
| Cody Milligan | .250 | .327 | .348 | 90 | 1.2 | .192 | .267 | .263 | 51 | -0.7 |
| Jair Camargo | .238 | .286 | .390 | 86 | 1.1 | .179 | .226 | .291 | 46 | -0.5 |
| Vidal Bruján | .254 | .321 | .373 | 95 | 1.1 | .201 | .263 | .283 | 55 | -0.4 |
| David McCabe | .257 | .330 | .402 | 103 | 1.2 | .204 | .278 | .317 | 68 | -1.0 |
| Eddy Alvarez | .236 | .327 | .385 | 98 | 1.0 | .178 | .271 | .279 | 58 | -0.6 |
| José Azocar | .269 | .313 | .377 | 94 | 1.1 | .214 | .258 | .290 | 56 | -0.6 |
| Chuckie Robinson | .259 | .307 | .356 | 87 | 1.1 | .198 | .243 | .271 | 48 | -0.5 |
| Jarred Kelenic | .255 | .316 | .423 | 105 | 1.1 | .203 | .264 | .327 | 66 | -1.2 |
| Jim Jarvis | .256 | .308 | .340 | 84 | 1.1 | .203 | .257 | .266 | 48 | -0.7 |
| Austin Nola | .250 | .315 | .354 | 88 | 0.4 | .187 | .254 | .264 | 49 | -0.5 |
| Garrett Cooper | .262 | .329 | .431 | 109 | 0.9 | .203 | .267 | .321 | 65 | -0.8 |
| Jose Devers | .263 | .320 | .376 | 94 | 0.7 | .205 | .259 | .287 | 54 | -0.6 |
| Chandler Seagle | .205 | .253 | .278 | 49 | 0.4 | .147 | .192 | .200 | 11 | -0.6 |
| David Fletcher | .249 | .290 | .314 | 71 | 0.8 | .190 | .233 | .242 | 34 | -0.8 |
| E.J. Exposito | .231 | .286 | .390 | 86 | 1.0 | .179 | .232 | .292 | 49 | -1.2 |
| Sandy León | .194 | .271 | .347 | 75 | 0.5 | .141 | .216 | .237 | 33 | -0.6 |
| Chadwick Tromp | .234 | .286 | .375 | 84 | 0.7 | .176 | .225 | .273 | 41 | -0.7 |
| Keshawn Ogans | .246 | .314 | .319 | 78 | 0.5 | .194 | .262 | .248 | 45 | -1.0 |
| Luke Williams | .229 | .289 | .360 | 81 | 0.8 | .176 | .233 | .271 | 42 | -0.8 |
| John Gil | .247 | .309 | .340 | 83 | 1.0 | .189 | .251 | .258 | 45 | -1.3 |
| Dylan Shockley | .205 | .285 | .247 | 50 | 0.0 | .138 | .217 | .166 | 11 | -0.7 |
| Kobe Kato | .213 | .313 | .322 | 79 | 0.3 | .161 | .257 | .237 | 42 | -0.8 |
| Matthew Batten | .227 | .289 | .351 | 80 | 0.7 | .176 | .238 | .263 | 43 | -1.4 |
| Will Verdung | .248 | .313 | .299 | 74 | 0.2 | .188 | .255 | .224 | 38 | -1.3 |
| Ambioris Tavarez | .225 | .296 | .312 | 70 | 0.3 | .168 | .242 | .229 | 34 | -1.6 |
| Cade Bunnell | .209 | .302 | .344 | 81 | 0.4 | .153 | .239 | .251 | 39 | -1.3 |
| Ethan Workinger | .251 | .304 | .395 | 93 | 0.4 | .197 | .251 | .302 | 57 | -1.8 |
| Drew Compton | .253 | .310 | .346 | 85 | 0.2 | .201 | .258 | .273 | 50 | -1.7 |
| Stephen Paolini | .223 | .292 | .330 | 76 | 0.1 | .160 | .232 | .241 | 37 | -1.5 |
| Patrick Clohisy | .256 | .312 | .347 | 84 | 0.5 | .206 | .263 | .274 | 54 | -1.8 |
| Joe Olsavsky | .216 | .321 | .290 | 75 | 0.0 | .164 | .264 | .216 | 40 | -1.3 |
| Adam Zebrowski | .227 | .284 | .353 | 76 | 0.1 | .171 | .229 | .263 | 38 | -1.6 |
| Justin Janas | .256 | .316 | .345 | 88 | 0.1 | .203 | .267 | .269 | 53 | -1.6 |
| Kevin Kilpatrick Jr. | .237 | .298 | .312 | 73 | 0.4 | .175 | .242 | .240 | 37 | -1.7 |
| Mac Guscette | .214 | .278 | .308 | 65 | -0.2 | .160 | .221 | .226 | 28 | -1.5 |
| Carlos Arroyo | .193 | .243 | .264 | 41 | -0.6 | .138 | .192 | .174 | 5 | -1.3 |
| Geraldo Quintero | .235 | .316 | .343 | 85 | -0.1 | .183 | .263 | .262 | 51 | -2.0 |
| Tyler Tolve | .210 | .260 | .346 | 67 | -0.4 | .152 | .205 | .250 | 28 | -1.6 |
| Jake Steels | .198 | .273 | .249 | 49 | -0.6 | .147 | .224 | .185 | 18 | -1.5 |
| Lizandro Espinoza | .205 | .257 | .356 | 68 | -0.2 | .159 | .211 | .263 | 34 | -2.1 |
| Cal Conley | .234 | .284 | .302 | 65 | -0.1 | .187 | .238 | .239 | 35 | -2.2 |
| Colby Jones | .224 | .298 | .260 | 60 | -0.1 | .168 | .246 | .202 | 30 | -2.1 |
| Isaiah Drake | .244 | .291 | .327 | 73 | -0.3 | .190 | .241 | .257 | 42 | -2.2 |
| Mason Guerra | .206 | .283 | .340 | 74 | -0.5 | .158 | .231 | .260 | 38 | -2.2 |
| Bryson Horne | .228 | .270 | .361 | 75 | -0.6 | .173 | .213 | .269 | 35 | -2.4 |
| Jace Grady | .207 | .271 | .286 | 57 | -1.3 | .156 | .216 | .211 | 22 | -2.6 |
| Player | BA vs. L | OBP vs. L | SLG vs. L | BA vs. R | OBP vs. R | SLG vs. R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ronald Acuña Jr. | .284 | .411 | .517 | .287 | .394 | .521 |
| Michael Harris II | .268 | .301 | .426 | .279 | .312 | .468 |
| Drake Baldwin | .259 | .333 | .440 | .267 | .343 | .478 |
| Matt Olson | .244 | .325 | .436 | .253 | .349 | .481 |
| Austin Riley | .268 | .333 | .488 | .260 | .322 | .474 |
| Sean Murphy | .229 | .324 | .469 | .222 | .313 | .413 |
| Marcell Ozuna | .254 | .355 | .449 | .247 | .343 | .444 |
| Ha-Seong Kim | .256 | .345 | .380 | .239 | .320 | .352 |
| Ozzie Albies | .275 | .317 | .430 | .240 | .307 | .394 |
| Jesús Bastidas | .230 | .302 | .385 | .227 | .298 | .367 |
| Brett Wisely | .236 | .301 | .374 | .246 | .314 | .375 |
| Nacho Alvarez Jr. | .241 | .325 | .339 | .235 | .313 | .321 |
| Eli White | .240 | .298 | .385 | .241 | .296 | .364 |
| Jurickson Profar | .258 | .350 | .411 | .249 | .345 | .405 |
| Charles Leblanc | .236 | .328 | .364 | .234 | .322 | .356 |
| Brewer Hicklen | .217 | .301 | .388 | .210 | .295 | .378 |
| Alex Verdugo | .240 | .294 | .336 | .256 | .316 | .392 |
| Conner Capel | .207 | .273 | .302 | .228 | .300 | .368 |
| Luke Waddell | .227 | .295 | .294 | .237 | .307 | .300 |
| Mauricio Dubón | .264 | .308 | .364 | .248 | .285 | .354 |
| Jake Marisnick | .220 | .292 | .373 | .211 | .275 | .367 |
| Jonathan Ornelas | .224 | .299 | .321 | .214 | .278 | .290 |
| Michael Siani | .204 | .276 | .292 | .204 | .280 | .294 |
| Cody Milligan | .208 | .284 | .292 | .230 | .304 | .311 |
| Jair Camargo | .214 | .264 | .340 | .207 | .251 | .341 |
| Vidal Bruján | .233 | .298 | .340 | .224 | .287 | .309 |
| David McCabe | .224 | .295 | .344 | .237 | .310 | .363 |
| Eddy Alvarez | .197 | .295 | .276 | .210 | .302 | .349 |
| José Azocar | .248 | .295 | .363 | .236 | .278 | .317 |
| Chuckie Robinson | .228 | .275 | .317 | .221 | .273 | .305 |
| Jarred Kelenic | .225 | .279 | .357 | .232 | .298 | .384 |
| Jim Jarvis | .207 | .270 | .250 | .234 | .288 | .316 |
| Austin Nola | .232 | .290 | .321 | .211 | .281 | .303 |
| Garrett Cooper | .241 | .304 | .398 | .227 | .291 | .360 |
| Jose Devers | .231 | .282 | .333 | .234 | .286 | .326 |
| Chandler Seagle | .172 | .221 | .219 | .176 | .220 | .244 |
| David Fletcher | .222 | .264 | .283 | .217 | .256 | .267 |
| E.J. Exposito | .213 | .271 | .333 | .205 | .256 | .340 |
| Sandy León | .175 | .254 | .316 | .156 | .243 | .273 |
| Chadwick Tromp | .213 | .268 | .326 | .199 | .249 | .311 |
| Keshawn Ogans | .221 | .292 | .295 | .219 | .285 | .279 |
| Luke Williams | .208 | .274 | .313 | .200 | .251 | .306 |
| John Gil | .220 | .290 | .288 | .212 | .274 | .298 |
| Dylan Shockley | .163 | .250 | .186 | .169 | .250 | .213 |
| Kobe Kato | .182 | .274 | .273 | .191 | .287 | .276 |
| Matthew Batten | .213 | .280 | .324 | .192 | .254 | .292 |
| Will Verdung | .214 | .287 | .274 | .220 | .284 | .257 |
| Ambioris Tavarez | .207 | .282 | .288 | .191 | .264 | .266 |
| Cade Bunnell | .171 | .256 | .267 | .180 | .270 | .300 |
| Ethan Workinger | .220 | .278 | .348 | .225 | .276 | .350 |
| Drew Compton | .231 | .283 | .308 | .227 | .287 | .313 |
| Stephen Paolini | .182 | .255 | .250 | .197 | .268 | .306 |
| Patrick Clohisy | .215 | .267 | .281 | .237 | .294 | .320 |
| Joe Olsavsky | .190 | .289 | .278 | .189 | .290 | .240 |
| Adam Zebrowski | .202 | .263 | .327 | .195 | .252 | .297 |
| Justin Janas | .222 | .293 | .289 | .232 | .291 | .310 |
| Kevin Kilpatrick Jr. | .214 | .279 | .291 | .201 | .264 | .267 |
| Mac Guscette | .195 | .259 | .299 | .180 | .240 | .246 |
| Carlos Arroyo | .170 | .220 | .213 | .158 | .218 | .218 |
| Geraldo Quintero | .208 | .284 | .308 | .213 | .293 | .302 |
| Tyler Tolve | .188 | .230 | .319 | .181 | .233 | .294 |
| Jake Steels | .182 | .257 | .212 | .168 | .245 | .217 |
| Lizandro Espinoza | .185 | .240 | .311 | .181 | .232 | .300 |
| Cal Conley | .212 | .257 | .269 | .209 | .259 | .273 |
| Colby Jones | .205 | .279 | .235 | .192 | .265 | .224 |
| Isaiah Drake | .209 | .254 | .273 | .216 | .271 | .290 |
| Mason Guerra | .185 | .264 | .296 | .178 | .250 | .296 |
| Bryson Horne | .192 | .234 | .279 | .202 | .243 | .319 |
| Jace Grady | .176 | .244 | .257 | .180 | .242 | .250 |
| Player | T | Age | W | L | ERA | G | GS | IP | H | ER | HR | BB | SO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chris Sale | L | 37 | 9 | 4 | 3.10 | 22 | 21 | 124.7 | 105 | 43 | 13 | 34 | 150 |
| Spencer Schwellenbach | R | 26 | 8 | 5 | 3.39 | 20 | 20 | 124.7 | 111 | 47 | 15 | 23 | 122 |
| Spencer Strider | R | 27 | 11 | 9 | 3.87 | 25 | 24 | 137.3 | 117 | 59 | 17 | 46 | 164 |
| Reynaldo López | R | 32 | 7 | 5 | 3.58 | 35 | 16 | 100.7 | 88 | 40 | 11 | 35 | 100 |
| Lucas Braun | R | 24 | 6 | 6 | 4.29 | 25 | 24 | 130.0 | 130 | 62 | 18 | 36 | 110 |
| Hurston Waldrep | R | 24 | 10 | 9 | 4.27 | 26 | 25 | 130.7 | 124 | 62 | 15 | 56 | 117 |
| Bryce Elder | R | 27 | 9 | 9 | 4.38 | 27 | 27 | 152.0 | 149 | 74 | 18 | 50 | 128 |
| AJ Smith-Shawver | R | 23 | 5 | 5 | 3.90 | 20 | 20 | 80.7 | 74 | 35 | 10 | 32 | 88 |
| JR Ritchie | R | 23 | 6 | 7 | 4.41 | 24 | 24 | 118.3 | 113 | 58 | 15 | 43 | 103 |
| Nathan Wiles | R | 27 | 6 | 5 | 4.30 | 24 | 16 | 96.3 | 102 | 46 | 13 | 23 | 73 |
| Dylan Dodd | L | 28 | 5 | 4 | 4.11 | 34 | 11 | 85.3 | 87 | 39 | 12 | 21 | 72 |
| José Suarez | L | 28 | 4 | 5 | 4.15 | 22 | 13 | 82.3 | 81 | 38 | 10 | 28 | 78 |
| Didier Fuentes | R | 21 | 6 | 7 | 4.45 | 21 | 21 | 87.0 | 84 | 43 | 12 | 29 | 82 |
| Jhancarlos Lara | R | 23 | 4 | 5 | 4.24 | 32 | 16 | 76.3 | 65 | 36 | 8 | 44 | 87 |
| Ian Mejia | R | 26 | 6 | 8 | 4.61 | 23 | 18 | 109.3 | 115 | 56 | 16 | 35 | 83 |
| Alek Manoah | R | 28 | 5 | 5 | 4.43 | 17 | 17 | 87.3 | 82 | 43 | 11 | 35 | 73 |
| Raisel Iglesias | R | 36 | 5 | 3 | 3.51 | 59 | 0 | 56.3 | 48 | 22 | 7 | 14 | 60 |
| Dylan Lee | L | 31 | 3 | 3 | 3.50 | 64 | 0 | 61.7 | 53 | 24 | 9 | 18 | 71 |
| Grant Holmes | R | 30 | 4 | 3 | 4.15 | 24 | 9 | 69.3 | 67 | 32 | 9 | 27 | 64 |
| Dane Dunning | R | 31 | 4 | 5 | 4.57 | 27 | 17 | 100.3 | 103 | 51 | 14 | 34 | 85 |
| Connor Thomas | L | 28 | 5 | 5 | 4.47 | 31 | 11 | 86.7 | 94 | 43 | 10 | 25 | 59 |
| Landon Harper | R | 25 | 5 | 6 | 4.63 | 24 | 12 | 89.3 | 94 | 46 | 14 | 23 | 65 |
| Joey Wentz | L | 28 | 5 | 5 | 4.53 | 33 | 12 | 89.3 | 89 | 45 | 11 | 37 | 88 |
| Charlie Morton | R | 42 | 7 | 9 | 4.88 | 25 | 22 | 120.0 | 117 | 65 | 18 | 57 | 121 |
| Ian Anderson | R | 28 | 4 | 6 | 4.57 | 17 | 13 | 67.0 | 69 | 34 | 8 | 31 | 51 |
| Brett Sears | R | 26 | 8 | 10 | 4.88 | 21 | 18 | 101.3 | 100 | 55 | 16 | 30 | 87 |
| Davis Daniel | R | 29 | 7 | 9 | 4.88 | 23 | 18 | 103.3 | 107 | 56 | 16 | 35 | 78 |
| Pierce Johnson | R | 35 | 4 | 2 | 3.83 | 55 | 0 | 49.3 | 46 | 21 | 6 | 19 | 55 |
| Blane Abeyta | R | 27 | 4 | 5 | 4.67 | 30 | 12 | 79.0 | 81 | 41 | 11 | 28 | 65 |
| Aaron Bummer | L | 32 | 3 | 2 | 3.75 | 42 | 1 | 48.0 | 45 | 20 | 4 | 19 | 50 |
| Zach Thompson | R | 32 | 4 | 4 | 4.82 | 20 | 12 | 65.3 | 71 | 35 | 9 | 25 | 45 |
| Tyler Kinley | R | 35 | 4 | 3 | 3.95 | 58 | 0 | 57.0 | 48 | 25 | 7 | 24 | 65 |
| Joel Payamps | R | 32 | 3 | 2 | 3.98 | 54 | 0 | 52.0 | 50 | 23 | 6 | 16 | 47 |
| Jackson Stephens | R | 32 | 2 | 3 | 4.19 | 24 | 3 | 43.0 | 43 | 20 | 5 | 13 | 35 |
| Carson Ragsdale | R | 28 | 5 | 7 | 4.88 | 24 | 18 | 83.0 | 85 | 45 | 12 | 38 | 71 |
| Blake Burkhalter | R | 25 | 4 | 5 | 4.93 | 26 | 14 | 84.0 | 88 | 46 | 13 | 31 | 63 |
| Drue Hackenberg | R | 24 | 4 | 7 | 5.17 | 21 | 21 | 87.0 | 88 | 50 | 11 | 47 | 67 |
| Anderson Pilar | R | 28 | 3 | 3 | 4.42 | 38 | 3 | 55.0 | 55 | 27 | 7 | 18 | 48 |
| Amos Willingham | R | 27 | 3 | 2 | 4.20 | 38 | 2 | 55.7 | 56 | 26 | 7 | 18 | 49 |
| Hayden Harris | L | 27 | 3 | 3 | 4.21 | 43 | 0 | 47.0 | 41 | 22 | 6 | 19 | 52 |
| Joe Jiménez | R | 31 | 2 | 2 | 4.23 | 41 | 0 | 38.3 | 34 | 18 | 5 | 15 | 44 |
| Cory Wall | R | 26 | 3 | 3 | 4.62 | 30 | 5 | 50.7 | 51 | 26 | 7 | 18 | 41 |
| Luis Vargas | R | 24 | 3 | 4 | 5.11 | 20 | 11 | 68.7 | 72 | 39 | 11 | 31 | 56 |
| Hunter Stratton | R | 29 | 3 | 2 | 4.25 | 44 | 0 | 53.0 | 51 | 25 | 7 | 19 | 49 |
| Connor Seabold | R | 30 | 3 | 5 | 5.01 | 26 | 12 | 79.0 | 85 | 44 | 11 | 26 | 63 |
| Brian Moran | L | 37 | 1 | 2 | 4.50 | 21 | 2 | 40.0 | 42 | 20 | 6 | 12 | 35 |
| Austin Cox | L | 29 | 3 | 3 | 4.82 | 36 | 7 | 71.0 | 73 | 38 | 10 | 28 | 56 |
| Chad Kuhl | R | 33 | 3 | 3 | 5.05 | 22 | 11 | 67.7 | 71 | 38 | 10 | 33 | 57 |
| Rolddy Munoz | R | 26 | 3 | 2 | 4.63 | 37 | 3 | 56.3 | 55 | 29 | 7 | 28 | 50 |
| Jake McSteen | L | 30 | 2 | 3 | 4.50 | 26 | 2 | 40.0 | 44 | 20 | 6 | 13 | 30 |
| Josh Walker | L | 31 | 2 | 2 | 4.32 | 37 | 0 | 41.7 | 41 | 20 | 5 | 18 | 40 |
| Daysbel Hernández | R | 29 | 3 | 4 | 4.47 | 44 | 0 | 44.3 | 38 | 22 | 5 | 26 | 47 |
| Jesse Chavez | R | 42 | 2 | 1 | 4.50 | 31 | 1 | 40.0 | 41 | 20 | 6 | 15 | 37 |
| Carlos Carrasco | R | 39 | 4 | 7 | 5.36 | 21 | 19 | 95.7 | 113 | 57 | 16 | 33 | 72 |
| Chasen Shreve | L | 35 | 1 | 2 | 4.74 | 13 | 2 | 19.0 | 20 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 17 |
| Ryan Rolison | L | 28 | 2 | 3 | 4.72 | 41 | 3 | 61.0 | 66 | 32 | 9 | 22 | 46 |
| Ryan Bourassa | R | 26 | 2 | 3 | 4.64 | 34 | 0 | 42.7 | 38 | 22 | 6 | 22 | 43 |
| Jacob Wallace | R | 27 | 3 | 3 | 4.74 | 34 | 1 | 43.7 | 41 | 23 | 6 | 24 | 43 |
| Alexis Díaz | R | 29 | 3 | 4 | 4.71 | 49 | 0 | 49.7 | 40 | 26 | 5 | 27 | 49 |
| Elison Joseph | R | 25 | 2 | 3 | 4.97 | 37 | 0 | 41.7 | 39 | 23 | 6 | 24 | 41 |
| LJ McDonough | R | 26 | 3 | 3 | 5.06 | 34 | 0 | 42.7 | 43 | 24 | 5 | 24 | 36 |
| Shay Schanaman | R | 26 | 3 | 4 | 5.00 | 29 | 0 | 36.0 | 37 | 20 | 5 | 17 | 28 |
| Tyler LaPorte | R | 29 | 3 | 3 | 4.95 | 34 | 0 | 43.7 | 46 | 24 | 6 | 19 | 33 |
| Jonathan Hughes | R | 29 | 1 | 3 | 5.24 | 25 | 0 | 34.3 | 38 | 20 | 5 | 16 | 22 |
| Player | IP | K/9 | BB/9 | HR/9 | BB% | K% | BABIP | ERA+ | 3ERA+ | FIP | ERA- | WAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chris Sale | 124.7 | 10.8 | 2.5 | 0.9 | 6.7% | 29.5% | .299 | 134 | 122 | 3.12 | 75 | 2.9 |
| Spencer Schwellenbach | 124.7 | 8.8 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 4.6% | 24.3% | .282 | 122 | 122 | 3.44 | 82 | 2.6 |
| Spencer Strider | 137.3 | 10.8 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 8.1% | 28.8% | .295 | 107 | 106 | 3.54 | 93 | 2.2 |
| Reynaldo López | 100.7 | 8.9 | 3.1 | 1.0 | 8.3% | 23.8% | .283 | 116 | 112 | 3.70 | 86 | 1.9 |
| Lucas Braun | 130.0 | 7.6 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 6.6% | 20.0% | .293 | 97 | 101 | 4.19 | 103 | 1.5 |
| Hurston Waldrep | 130.7 | 8.1 | 3.9 | 1.0 | 9.8% | 20.5% | .291 | 97 | 100 | 4.27 | 103 | 1.5 |
| Bryce Elder | 152.0 | 7.6 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 7.7% | 19.7% | .292 | 95 | 96 | 4.12 | 105 | 1.5 |
| AJ Smith-Shawver | 80.7 | 9.8 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 9.2% | 25.3% | .300 | 106 | 111 | 3.86 | 94 | 1.2 |
| JR Ritchie | 118.3 | 7.8 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 8.5% | 20.4% | .287 | 94 | 99 | 4.39 | 106 | 1.2 |
| Nathan Wiles | 96.3 | 6.8 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 5.6% | 17.8% | .299 | 97 | 98 | 4.21 | 103 | 1.0 |
| Dylan Dodd | 85.3 | 7.6 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 5.8% | 19.9% | .296 | 101 | 103 | 4.11 | 99 | 0.9 |
| José Suarez | 82.3 | 8.5 | 3.1 | 1.1 | 8.0% | 22.2% | .303 | 100 | 101 | 3.98 | 100 | 0.9 |
| Didier Fuentes | 87.0 | 8.5 | 3.0 | 1.2 | 7.8% | 21.9% | .294 | 93 | 99 | 4.28 | 107 | 0.9 |
| Jhancarlos Lara | 76.3 | 10.3 | 5.2 | 0.9 | 12.9% | 25.6% | .294 | 98 | 106 | 4.33 | 102 | 0.8 |
| Ian Mejia | 109.3 | 6.8 | 2.9 | 1.3 | 7.4% | 17.5% | .295 | 90 | 94 | 4.67 | 111 | 0.8 |
| Alek Manoah | 87.3 | 7.5 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 9.3% | 19.5% | .281 | 94 | 94 | 4.61 | 106 | 0.8 |
| Raisel Iglesias | 56.3 | 9.6 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 6.1% | 26.3% | .281 | 118 | 109 | 3.50 | 85 | 0.8 |
| Dylan Lee | 61.7 | 10.4 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 7.1% | 28.1% | .286 | 119 | 116 | 3.63 | 84 | 0.7 |
| Grant Holmes | 69.3 | 8.3 | 3.5 | 1.2 | 9.0% | 21.3% | .294 | 100 | 98 | 4.35 | 100 | 0.7 |
| Dane Dunning | 100.3 | 7.6 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 7.8% | 19.5% | .299 | 91 | 89 | 4.48 | 110 | 0.7 |
| Connor Thomas | 86.7 | 6.1 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 6.7% | 15.8% | .302 | 93 | 95 | 4.31 | 107 | 0.6 |
| Landon Harper | 89.3 | 6.5 | 2.3 | 1.4 | 6.0% | 17.1% | .290 | 90 | 94 | 4.55 | 112 | 0.5 |
| Joey Wentz | 89.3 | 8.9 | 3.7 | 1.1 | 9.5% | 22.5% | .310 | 92 | 93 | 4.10 | 109 | 0.5 |
| Charlie Morton | 120.0 | 9.1 | 4.3 | 1.4 | 10.8% | 22.9% | .300 | 85 | 81 | 4.82 | 118 | 0.5 |
| Ian Anderson | 67.0 | 6.9 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 10.3% | 16.9% | .296 | 91 | 92 | 4.63 | 110 | 0.5 |
| Brett Sears | 101.3 | 7.7 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 7.0% | 20.4% | .286 | 85 | 89 | 4.65 | 118 | 0.5 |
| Davis Daniel | 103.3 | 6.8 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 7.8% | 17.4% | .289 | 85 | 86 | 4.80 | 117 | 0.4 |
| Pierce Johnson | 49.3 | 10.0 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 8.9% | 25.8% | .308 | 108 | 100 | 3.73 | 93 | 0.4 |
| Blane Abeyta | 79.0 | 7.4 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 8.2% | 19.0% | .297 | 89 | 92 | 4.66 | 112 | 0.4 |
| Aaron Bummer | 48.0 | 9.4 | 3.6 | 0.8 | 9.2% | 24.2% | .311 | 111 | 105 | 3.66 | 90 | 0.4 |
| Zach Thompson | 65.3 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 1.2 | 8.6% | 15.5% | .298 | 86 | 84 | 4.86 | 116 | 0.3 |
| Tyler Kinley | 57.0 | 10.3 | 3.8 | 1.1 | 9.8% | 26.6% | .287 | 105 | 97 | 3.85 | 95 | 0.3 |
| Joel Payamps | 52.0 | 8.1 | 2.8 | 1.0 | 7.3% | 21.5% | .295 | 104 | 101 | 3.89 | 96 | 0.3 |
| Jackson Stephens | 43.0 | 7.3 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 7.1% | 19.2% | .295 | 99 | 94 | 4.16 | 101 | 0.3 |
| Carson Ragsdale | 83.0 | 7.7 | 4.1 | 1.3 | 10.3% | 19.3% | .298 | 85 | 86 | 4.85 | 117 | 0.3 |
| Blake Burkhalter | 84.0 | 6.8 | 3.3 | 1.4 | 8.4% | 17.0% | .291 | 84 | 89 | 4.93 | 119 | 0.3 |
| Drue Hackenberg | 87.0 | 6.9 | 4.9 | 1.1 | 11.9% | 16.9% | .292 | 80 | 85 | 5.16 | 125 | 0.2 |
| Anderson Pilar | 55.0 | 7.9 | 2.9 | 1.1 | 7.6% | 20.2% | .298 | 94 | 95 | 4.38 | 106 | 0.2 |
| Amos Willingham | 55.7 | 7.9 | 2.9 | 1.1 | 7.5% | 20.5% | .301 | 99 | 102 | 4.12 | 101 | 0.2 |
| Hayden Harris | 47.0 | 10.0 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 9.5% | 26.0% | .289 | 99 | 103 | 4.08 | 101 | 0.2 |
| Joe Jiménez | 38.3 | 10.3 | 3.5 | 1.2 | 9.2% | 27.0% | .296 | 98 | 96 | 3.89 | 102 | 0.1 |
| Cory Wall | 50.7 | 7.3 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 8.2% | 18.6% | .291 | 90 | 93 | 4.64 | 111 | 0.1 |
| Luis Vargas | 68.7 | 7.3 | 4.1 | 1.4 | 10.0% | 18.1% | .296 | 81 | 88 | 5.14 | 123 | 0.1 |
| Hunter Stratton | 53.0 | 8.3 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 8.3% | 21.5% | .293 | 98 | 99 | 4.33 | 102 | 0.1 |
| Connor Seabold | 79.0 | 7.2 | 3.0 | 1.3 | 7.5% | 18.1% | .306 | 83 | 83 | 4.63 | 120 | 0.1 |
| Brian Moran | 40.0 | 7.9 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 6.9% | 20.2% | .305 | 92 | 83 | 4.56 | 109 | 0.1 |
| Austin Cox | 71.0 | 7.1 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 8.9% | 17.9% | .293 | 86 | 88 | 4.73 | 116 | 0.1 |
| Chad Kuhl | 67.7 | 7.6 | 4.4 | 1.3 | 10.7% | 18.6% | .302 | 82 | 78 | 5.08 | 122 | 0.1 |
| Rolddy Munoz | 56.3 | 8.0 | 4.5 | 1.1 | 11.1% | 19.8% | .294 | 90 | 93 | 4.71 | 111 | 0.1 |
| Jake McSteen | 40.0 | 6.8 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 7.4% | 17.0% | .304 | 92 | 91 | 4.59 | 108 | 0.0 |
| Josh Walker | 41.7 | 8.6 | 3.9 | 1.1 | 9.8% | 21.9% | .305 | 96 | 94 | 4.24 | 104 | 0.0 |
| Daysbel Hernández | 44.3 | 9.5 | 5.3 | 1.0 | 13.2% | 23.9% | .284 | 93 | 93 | 4.47 | 107 | 0.0 |
| Jesse Chavez | 40.0 | 8.3 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 8.7% | 21.4% | .304 | 92 | 89 | 4.46 | 109 | 0.0 |
| Carlos Carrasco | 95.7 | 6.8 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 7.7% | 16.8% | .318 | 77 | 75 | 5.02 | 130 | 0.0 |
| Chasen Shreve | 19.0 | 8.1 | 3.3 | 1.4 | 8.3% | 20.2% | .304 | 88 | 77 | 4.69 | 114 | 0.0 |
| Ryan Rolison | 61.0 | 6.8 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 8.2% | 17.1% | .302 | 88 | 89 | 4.70 | 114 | 0.0 |
| Ryan Bourassa | 42.7 | 9.1 | 4.6 | 1.3 | 11.3% | 22.2% | .281 | 90 | 94 | 4.66 | 112 | -0.1 |
| Jacob Wallace | 43.7 | 8.9 | 4.9 | 1.2 | 12.1% | 21.7% | .292 | 88 | 89 | 4.77 | 114 | -0.1 |
| Alexis Díaz | 49.7 | 8.9 | 4.9 | 0.9 | 12.5% | 22.7% | .265 | 88 | 88 | 4.55 | 113 | -0.2 |
| Elison Joseph | 41.7 | 8.9 | 5.2 | 1.3 | 12.4% | 21.2% | .289 | 84 | 89 | 5.01 | 120 | -0.3 |
| LJ McDonough | 42.7 | 7.6 | 5.1 | 1.1 | 12.2% | 18.3% | .299 | 82 | 86 | 4.90 | 122 | -0.3 |
| Shay Schanaman | 36.0 | 7.0 | 4.3 | 1.3 | 10.4% | 17.2% | .294 | 83 | 86 | 5.16 | 120 | -0.3 |
| Tyler LaPorte | 43.7 | 6.8 | 3.9 | 1.2 | 9.8% | 17.1% | .296 | 84 | 86 | 4.88 | 119 | -0.3 |
| Jonathan Hughes | 34.3 | 5.8 | 4.2 | 1.3 | 10.2% | 14.0% | .297 | 79 | 78 | 5.35 | 127 | -0.4 |
| Player | BA vs. L | OBP vs. L | SLG vs. L | BA vs. R | OBP vs. R | SLG vs. R | 80th WAR | 20th WAR | 80th ERA | 20th ERA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chris Sale | .208 | .267 | .271 | .227 | .290 | .379 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 2.36 | 4.15 |
| Spencer Schwellenbach | .248 | .295 | .419 | .223 | .258 | .353 | 3.5 | 1.9 | 2.84 | 3.78 |
| Spencer Strider | .238 | .307 | .402 | .211 | .280 | .345 | 3.4 | 1.1 | 3.21 | 4.56 |
| Reynaldo López | .234 | .317 | .386 | .231 | .280 | .364 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 2.94 | 4.20 |
| Lucas Braun | .243 | .301 | .407 | .262 | .308 | .432 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 3.67 | 4.92 |
| Hurston Waldrep | .249 | .336 | .408 | .239 | .310 | .379 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 3.84 | 4.90 |
| Bryce Elder | .255 | .323 | .429 | .246 | .303 | .377 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 3.84 | 4.94 |
| AJ Smith-Shawver | .229 | .299 | .369 | .238 | .313 | .394 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 3.31 | 4.71 |
| JR Ritchie | .248 | .331 | .420 | .246 | .311 | .388 | 2.0 | 0.4 | 3.89 | 4.98 |
| Nathan Wiles | .275 | .325 | .445 | .255 | .294 | .417 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 3.72 | 4.88 |
| Dylan Dodd | .245 | .279 | .367 | .263 | .312 | .450 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 3.51 | 4.88 |
| José Suarez | .236 | .310 | .371 | .254 | .314 | .415 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 3.61 | 5.04 |
| Didier Fuentes | .238 | .309 | .407 | .250 | .314 | .413 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 3.71 | 5.24 |
| Jhancarlos Lara | .225 | .347 | .359 | .221 | .335 | .356 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 3.70 | 5.01 |
| Ian Mejia | .268 | .335 | .470 | .261 | .315 | .408 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 4.05 | 5.18 |
| Alek Manoah | .273 | .362 | .459 | .216 | .293 | .352 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 3.92 | 5.05 |
| Raisel Iglesias | .250 | .306 | .410 | .209 | .261 | .355 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 2.56 | 4.82 |
| Dylan Lee | .217 | .258 | .373 | .235 | .294 | .409 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 2.69 | 4.53 |
| Grant Holmes | .250 | .331 | .367 | .248 | .318 | .440 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 3.62 | 4.86 |
| Dane Dunning | .271 | .343 | .452 | .248 | .307 | .405 | 1.3 | -0.1 | 4.01 | 5.29 |
| Connor Thomas | .259 | .304 | .405 | .274 | .331 | .427 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 4.01 | 5.14 |
| Landon Harper | .268 | .314 | .452 | .261 | .304 | .442 | 1.2 | -0.1 | 4.03 | 5.23 |
| Joey Wentz | .259 | .328 | .411 | .246 | .319 | .402 | 1.2 | -0.3 | 3.91 | 5.44 |
| Charlie Morton | .254 | .366 | .460 | .245 | .322 | .392 | 1.3 | -0.6 | 4.20 | 5.85 |
| Ian Anderson | .231 | .313 | .369 | .287 | .359 | .449 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 4.10 | 5.22 |
| Brett Sears | .273 | .344 | .471 | .237 | .295 | .406 | 1.3 | -0.3 | 4.20 | 5.58 |
| Davis Daniel | .272 | .340 | .450 | .252 | .310 | .436 | 1.1 | -0.3 | 4.37 | 5.48 |
| Pierce Johnson | .233 | .313 | .384 | .243 | .305 | .393 | 1.0 | -0.2 | 2.94 | 5.12 |
| Blane Abeyta | .282 | .356 | .458 | .240 | .311 | .409 | 0.9 | -0.3 | 4.16 | 5.44 |
| Aaron Bummer | .214 | .276 | .300 | .252 | .348 | .395 | 0.8 | -0.1 | 2.97 | 4.81 |
| Zach Thompson | .276 | .362 | .472 | .266 | .318 | .424 | 0.7 | -0.1 | 4.25 | 5.37 |
| Tyler Kinley | .210 | .307 | .370 | .237 | .307 | .386 | 1.0 | -0.4 | 3.08 | 5.22 |
| Joel Payamps | .247 | .309 | .435 | .248 | .305 | .368 | 0.7 | -0.2 | 3.28 | 4.97 |
| Jackson Stephens | .275 | .341 | .438 | .233 | .293 | .378 | 0.6 | -0.1 | 3.62 | 4.90 |
| Carson Ragsdale | .247 | .341 | .433 | .265 | .335 | .431 | 0.9 | -0.4 | 4.34 | 5.54 |
| Blake Burkhalter | .281 | .356 | .456 | .246 | .306 | .434 | 0.8 | -0.4 | 4.39 | 5.57 |
| Drue Hackenberg | .259 | .363 | .420 | .253 | .349 | .412 | 0.7 | -0.4 | 4.68 | 5.70 |
| Anderson Pilar | .245 | .324 | .357 | .261 | .326 | .454 | 0.6 | -0.3 | 3.79 | 5.15 |
| Amos Willingham | .263 | .330 | .411 | .246 | .299 | .405 | 0.7 | -0.2 | 3.51 | 4.99 |
| Hayden Harris | .217 | .309 | .350 | .237 | .321 | .407 | 0.6 | -0.3 | 3.43 | 5.04 |
| Joe Jiménez | .227 | .320 | .394 | .235 | .300 | .395 | 0.5 | -0.3 | 3.21 | 5.48 |
| Cory Wall | .269 | .355 | .462 | .243 | .299 | .383 | 0.5 | -0.2 | 4.01 | 5.24 |
| Luis Vargas | .262 | .349 | .469 | .262 | .337 | .434 | 0.6 | -0.5 | 4.57 | 5.81 |
| Hunter Stratton | .283 | .362 | .467 | .221 | .288 | .363 | 0.5 | -0.4 | 3.60 | 5.11 |
| Connor Seabold | .269 | .347 | .462 | .264 | .318 | .417 | 0.6 | -0.4 | 4.47 | 5.71 |
| Brian Moran | .250 | .333 | .411 | .269 | .325 | .462 | 0.4 | -0.4 | 3.64 | 5.86 |
| Austin Cox | .258 | .320 | .398 | .262 | .338 | .455 | 0.6 | -0.4 | 4.29 | 5.57 |
| Chad Kuhl | .263 | .365 | .474 | .263 | .338 | .416 | 0.5 | -0.4 | 4.49 | 5.74 |
| Rolddy Munoz | .267 | .364 | .465 | .231 | .319 | .347 | 0.5 | -0.4 | 4.01 | 5.37 |
| Jake McSteen | .231 | .273 | .327 | .288 | .344 | .505 | 0.4 | -0.3 | 3.78 | 5.26 |
| Josh Walker | .218 | .317 | .345 | .264 | .333 | .427 | 0.4 | -0.4 | 3.60 | 5.23 |
| Daysbel Hernández | .230 | .337 | .392 | .226 | .342 | .366 | 0.5 | -0.5 | 3.72 | 5.48 |
| Jesse Chavez | .257 | .337 | .432 | .256 | .309 | .430 | 0.4 | -0.4 | 3.66 | 5.82 |
| Carlos Carrasco | .282 | .349 | .479 | .287 | .341 | .474 | 0.5 | -0.8 | 4.75 | 6.24 |
| Chasen Shreve | .250 | .323 | .393 | .271 | .333 | .458 | 0.2 | -0.2 | 3.98 | 5.81 |
| Ryan Rolison | .284 | .324 | .493 | .261 | .328 | .422 | 0.3 | -0.5 | 4.13 | 5.36 |
| Ryan Bourassa | .256 | .363 | .449 | .217 | .305 | .373 | 0.2 | -0.5 | 4.06 | 5.44 |
| Jacob Wallace | .253 | .349 | .453 | .232 | .333 | .368 | 0.2 | -0.6 | 4.08 | 5.66 |
| Alexis Díaz | .232 | .370 | .378 | .212 | .319 | .343 | 0.3 | -0.7 | 4.04 | 5.62 |
| Elison Joseph | .257 | .368 | .392 | .230 | .333 | .437 | 0.1 | -0.7 | 4.34 | 5.79 |
| LJ McDonough | .256 | .365 | .415 | .247 | .340 | .393 | 0.0 | -0.7 | 4.49 | 5.75 |
| Shay Schanaman | .288 | .390 | .439 | .237 | .322 | .434 | -0.1 | -0.6 | 4.50 | 5.74 |
| Tyler LaPorte | .282 | .371 | .471 | .244 | .310 | .400 | 0.0 | -0.7 | 4.31 | 5.88 |
| Jonathan Hughes | .286 | .357 | .476 | .267 | .356 | .440 | -0.1 | -0.7 | 4.62 | 6.03 |
Players are listed with their most recent teams wherever possible. This includes players who are unsigned or have retired, players who will miss 2026 due to injury, and players who were released in 2025. So yes, if you see Joe Schmoe, who quit baseball back in August to form a Ambient Math-Rock Trip-Hop Yacht Metal band that only performs in abandoned malls, he’s still listed here intentionally. ZiPS is assuming a league with an ERA of 4.16.
Hitters are ranked by zWAR, which is to say, WAR values as calculated by me, Dan Szymborski, whose surname is spelled with a z. WAR values might differ slightly from those that appear in the full release of ZiPS. Finally, I will advise anyone against — and might karate chop anyone guilty of — merely adding up WAR totals on a depth chart to produce projected team WAR. It is important to remember that ZiPS is agnostic about playing time, and has no information about, for example, how quickly a team will call up a prospect or what veteran has fallen into disfavor.
As always, incorrect projections are either caused by misinformation, a non-pragmatic reality, or by the skillful sabotage of our friend and former editor. You can, however, still get mad at me on Twitter or on BlueSky. This last is, however, not an actual requirement.






